Conclusions » History » Version 11
« Previous -
Version 11/15
(diff) -
Next » -
Current version
HAENNIG, Gerald, 12/15/2015 10:46 AM
5. Conclusions¶
h2 5.1 Simplified optical link model for transmission of a carrier
The model is based on the Spurious Free Dynamic Range :
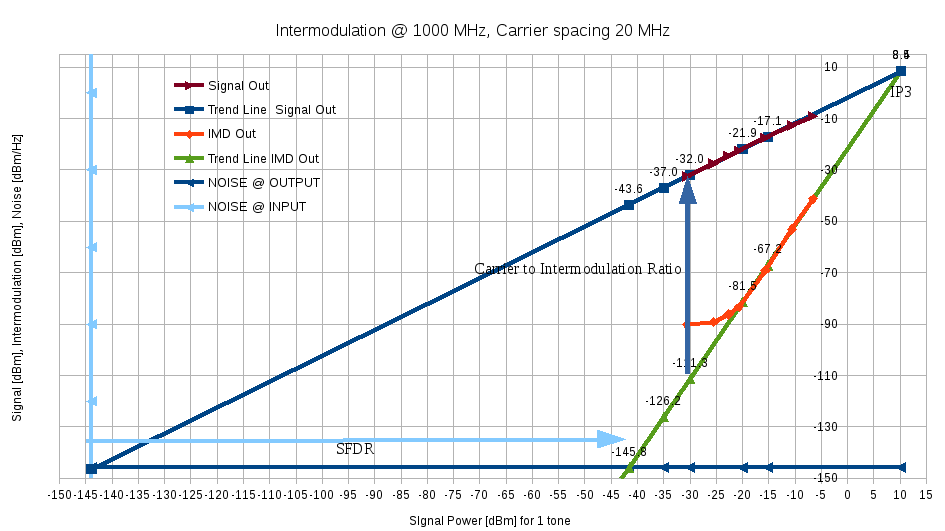
Figure 2. RF frequency respone (for several RF input powers).
- RF output power
5.2 Link comparison : Optical link vs Coaxial Cable for 30 m link length (like in a home)¶
In the following table, there is a comparison between coaxial cable to optical link.
| Parameter | Coaxial Cable | Optical Link |
|---|---|---|
| RF Gain @ 950 MHz [dB] | -3.6 | +0.5 |
| RF Gain @ 2150 MHz [dB] | -5.6 | +3.0 |
| Noise Figure @ 950 MHz [dB] | +3.6 | +30 |
| Noise Figure @ 2150 MHz | +5.6 | +33 |
| IIP3 [dBm] | +50 | +10 |
| SFDR [dB/Hz2/3] | +145 | +102 |
| LNB remote supply | Yes, supplied through coaxial cable | No, supply close to antenna for OTX required |
| Current Consumption [mA] | 0 | 700 mA / 12 V |
| LNB telecommand | Yes | No |
| Bidirectional link | Yes | Yes, but with additional hardware |
| Cost | Low | High |
For a distance of 30 m, optical link is not justified : performances and cost are not competitive with coaxial cable.
