Mission Payload earth station and Link Bidget¶
Main parameters and characteristics (Payload, earth station)
According to the NASA’s website, Voyager 1 is navigating on 20h:06 of 10/03/2016 at 134,271,078 AU, which corresponds to 20,086,735,880 km from the earth with a velocity reaching 17,061 m/s.
The light round trip from to the probe takes 37h:13min:24s that means that in order to send a command from earth and to know the response behavior of the probe we will wait one and a half day.
The probe is using 2 frequencies. One at f1=8.42 GHz (X-band), and the second at f2=2.307 GHz(S-band). More precisely, the frequency used for Down link these days is 8420.432 MHz.
Thus, BPSK modulation is used which conduct to a very low throughput equal 16 bit/s for the Up link and 160 bit/s - 1.4 Kbit/s for the Down link.
Link Budget
One of the main issues for such communication systems is the high free space loss and the low power transmitting from the probe. In this case, the power transmitted is 12/18 w in low/high power mode.
And as that the free space loss formula is:
L = 10*log((4*pi*d)/lambda)^2
L = 10*log((4*pi*20,086,735,880*10^3)/(3*10^8/8.33*10^9))^2 = 317 dB ! It is the losses value of the link from the current probe localization.
Also, L was equal 278.8 dB during Mars phase where the distance from earth was 2.5 AU comparing with 100 AU in current position.
So, it is clear that these losses represent one of the major problems to deal with in order to establish a reliable communication.
The antenna used has a diameter equal to 3.74 m and a gain equal to 48.2 dB.
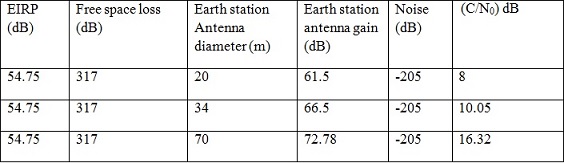
This leads to calculate the EIRP = 10*log(18) + 48.2 = 60.75 dB (1.18 Mw). But taking into account carrier suppression losses (-6dB). The final EIRP = 60.75-6=54.75 dB (298.53 Kw).
Concerning the earth station antenna, several one are used.
If D=20, with efficiency = 55% ==> G=61.9 dB
If D=34, with efficiency = 55% ==> G=66.51 dB
If D=70, with efficiency = 55% ==> G=72.78 dB
In such communication system, the main factor is C/N0 rate. Below, you find the calculation detailed for this rate.
Moon noise is an important factor to take into account in space communication. N0=3.3dB ==> T=189 K.
N = N0.B = K.T.B= 1,379.10^-23 .189= -205 dBw.
With B=1Hz.
As mentioned before, D = 20,086,735,880 km
and (C/N0)D = EIRPSAT * (1/L) * (1/K) * (G/T)ES
For D=20 m, (G/T)ES = 10^6.15/189=39 dB.
For D=34 m, (G/T)ES = 10^6.65/189= 43 dB.
For D=70 m, (G/T)ES = 10^7/189= 47.23 dB.
(C/N0)T = Eb/N0 * Rb
For Rb = 160 bps
Eb/N0 = 16.32 – 22.04 = -5.72 + 6 = 0.28 dBHz
For Rb = 1.4 Kbps
Eb/N0 = 16.32 – 31.46 = -15.14 + 6 = -9.14 dBHz
References
